Association vs Inheritance - Class Relationships
- 5 minsWhen designing object-oriented systems, understanding how classes relate to each other is crucial. Some design patterns emphasize inheritance-based relationships, while others use composition or aggregation to model how objects interact. Each of these relationships serves a different purpose and has unique implications for system design.
I’ve decided to write this because I was studying design patterns and realized I needed to deepen my understanding of the different types of relationships between classes, particularly how they impact system design and flexibility.
Association
Association is a generic term that refers to the relationship between two independent classes. It represents a “uses-a” relationship, meaning that one object interacts with another object without necessarily owning it.
Characteristics of Association:
- Can be unidirectional (only one class knows about the relationship) or bidirectional (both classes are aware of each other).
- Can be categorized into different types based on cardinality:
- One-to-One
- One-to-Many
- Many-to-Many
- Does not imply ownership.
Example of Association
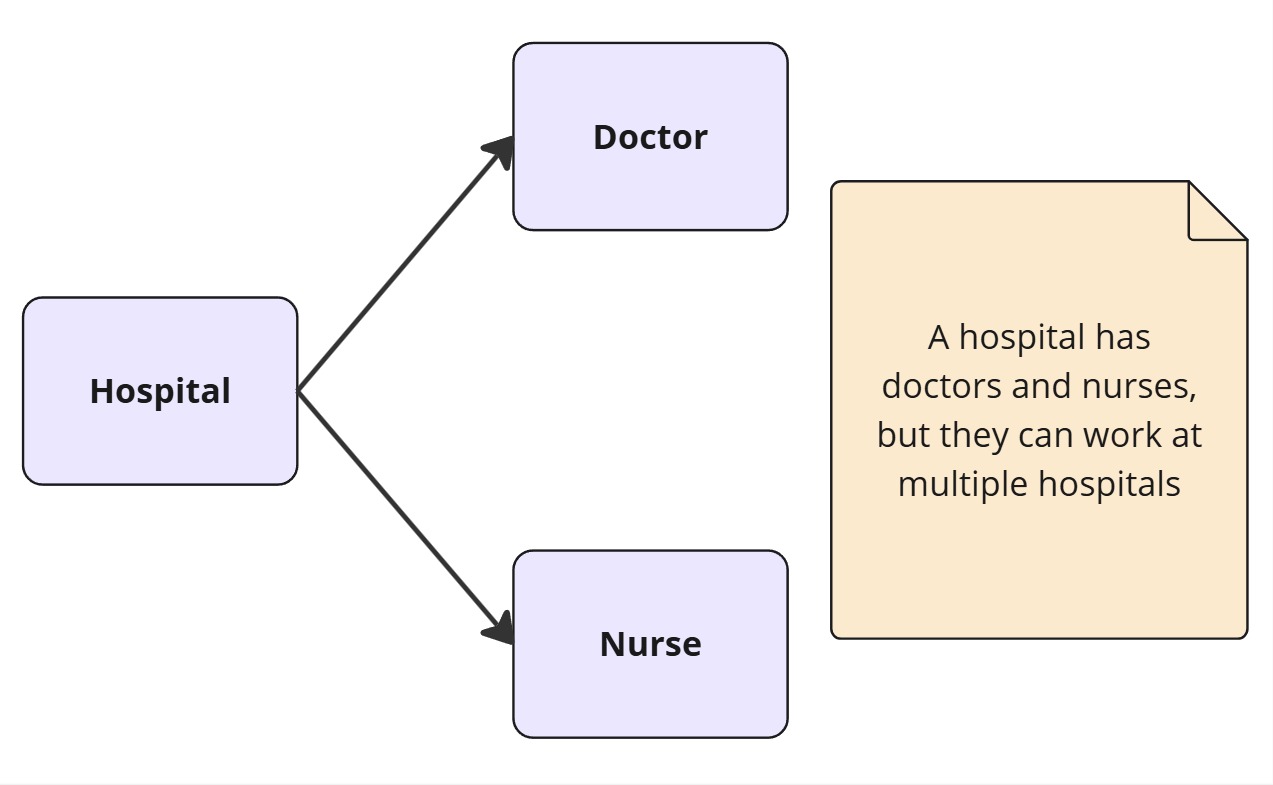
Design Patterns Using Association
- Mediator Pattern: Defines an intermediary object that encapsulates how a set of objects interact, reducing direct dependencies.
- Facade Pattern: Provides a simplified interface to a larger body of code, managing interactions between multiple objects.
Aggregation
Aggregation is a specific type of association where one class contains a collection of other classes. This relationship is often referred to as a “has-a” relationship and is used in design patterns that require flexible structures where components can exist independently.
Characteristics of Aggregation:
- The container object can exist independently of its contents, and vice versa.
- It is a unidirectional relationship.
- If the container object is deleted, the contained objects can still exist independently.
Example of Aggregation
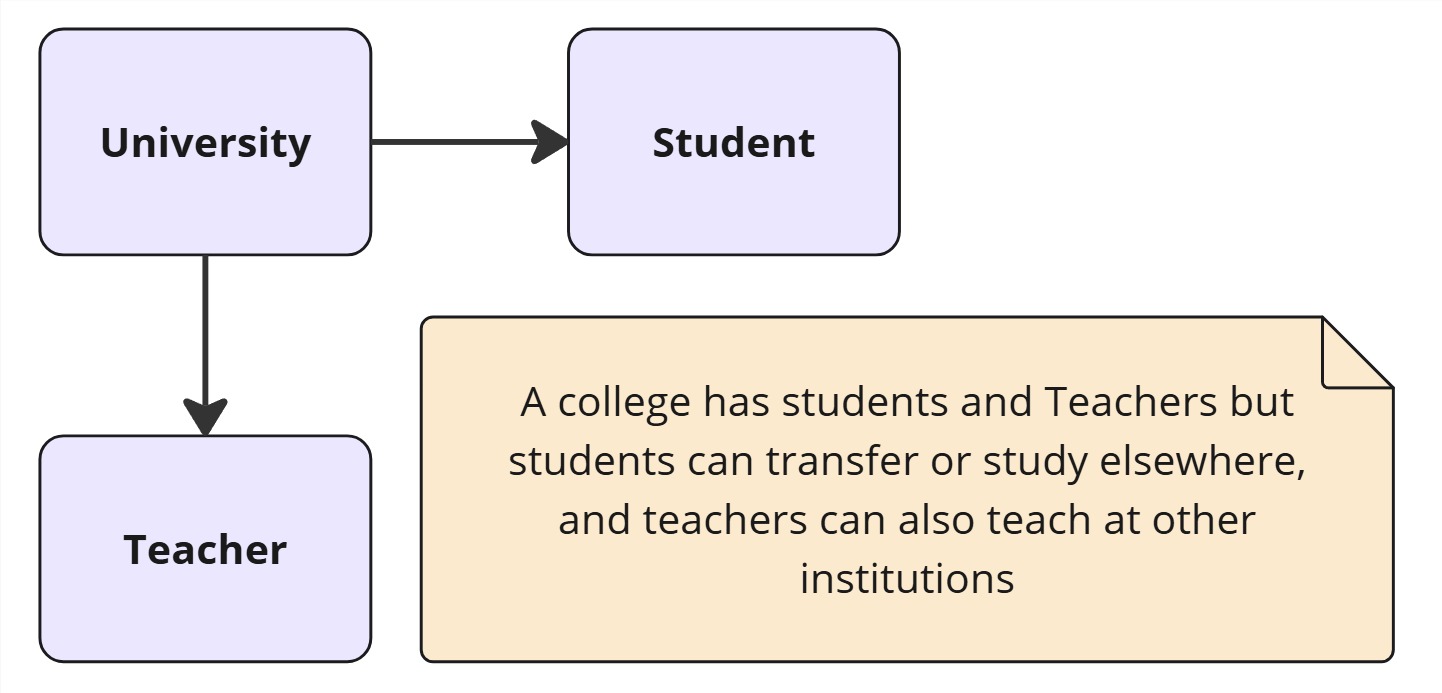
Design Patterns Using Aggregation
- Observer Pattern: Defines a one-to-many dependency, allowing multiple observers to listen for changes in a subject without being tightly coupled. In a design pattern such as the Observer pattern, a subject maintains a list of observers that may receive updates. The subject exists independently, and observers can be detached at any time.
- Builder Pattern: Constructs complex objects step by step by aggregating smaller components into a whole.
Composition
Composition is a stronger form of aggregation, meaning that the contained objects’ lifecycle is dependent on the container object’s lifecycle. This is often used in design patterns where strict ownership and dependency are required.
Characteristics of Composition:
- Implies ownership: the container class owns the contained objects.
- The contained objects cannot exist independently.
- If the container object is destroyed, the contained objects are also destroyed.
Example of Composition
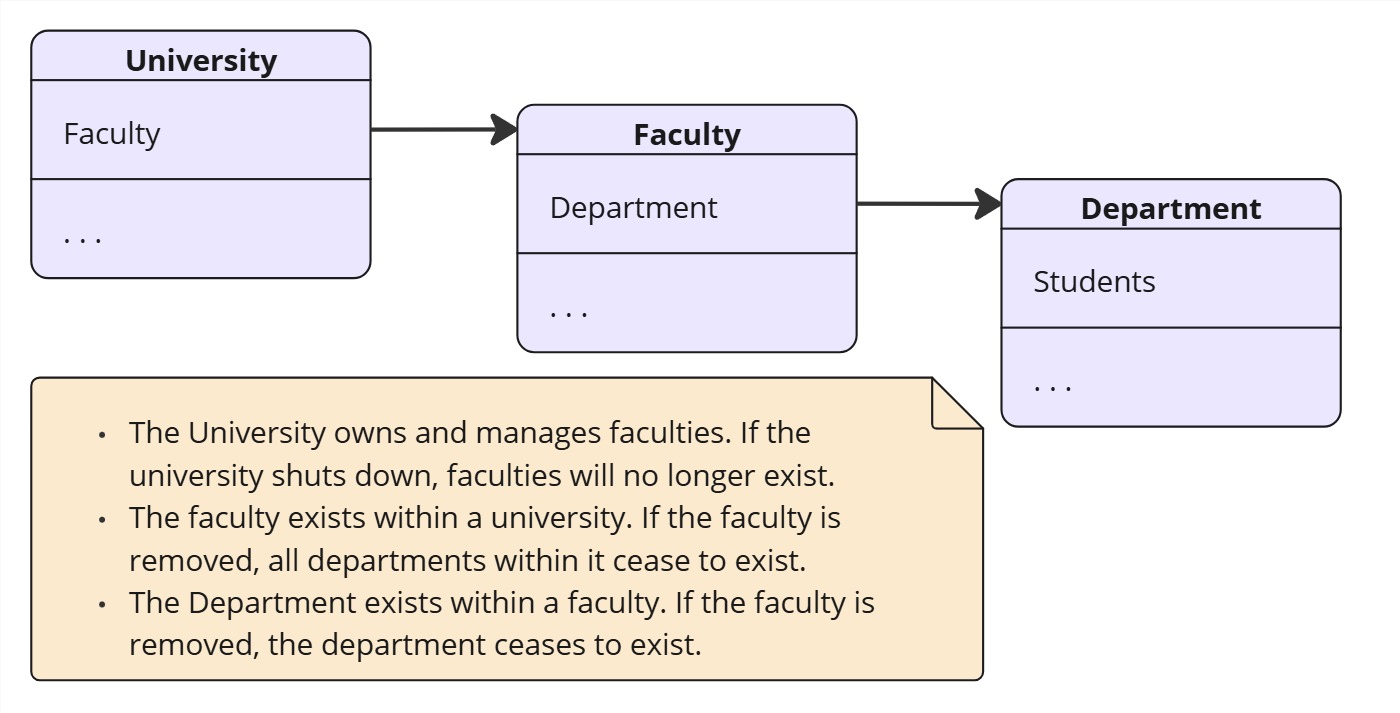
Design Patterns Using Composition
- Strategy Pattern: Uses composition to dynamically change the behavior of a class by switching strategies at runtime. In this pattern, a context contains a strategy object that defines its behavior. The strategy object only exists as part of the context and is replaced when a different strategy is needed.
- Decorator Pattern: Wraps objects within other objects to dynamically enhance their behavior without modifying the base class.
Inheritance
Inheritance is a mechanism that allows one class (subclass) to acquire properties and behaviors from another class (superclass). It establishes an “is-a” relationship and is commonly used in design patterns that rely on class hierarchies.
Characteristics of Inheritance:
- Defines a hierarchical relationship.
- The child class (subclass) inherits fields and methods from the parent class (superclass).
- Allows method overriding to provide specialized behavior in subclasses.
Example of Inheritance
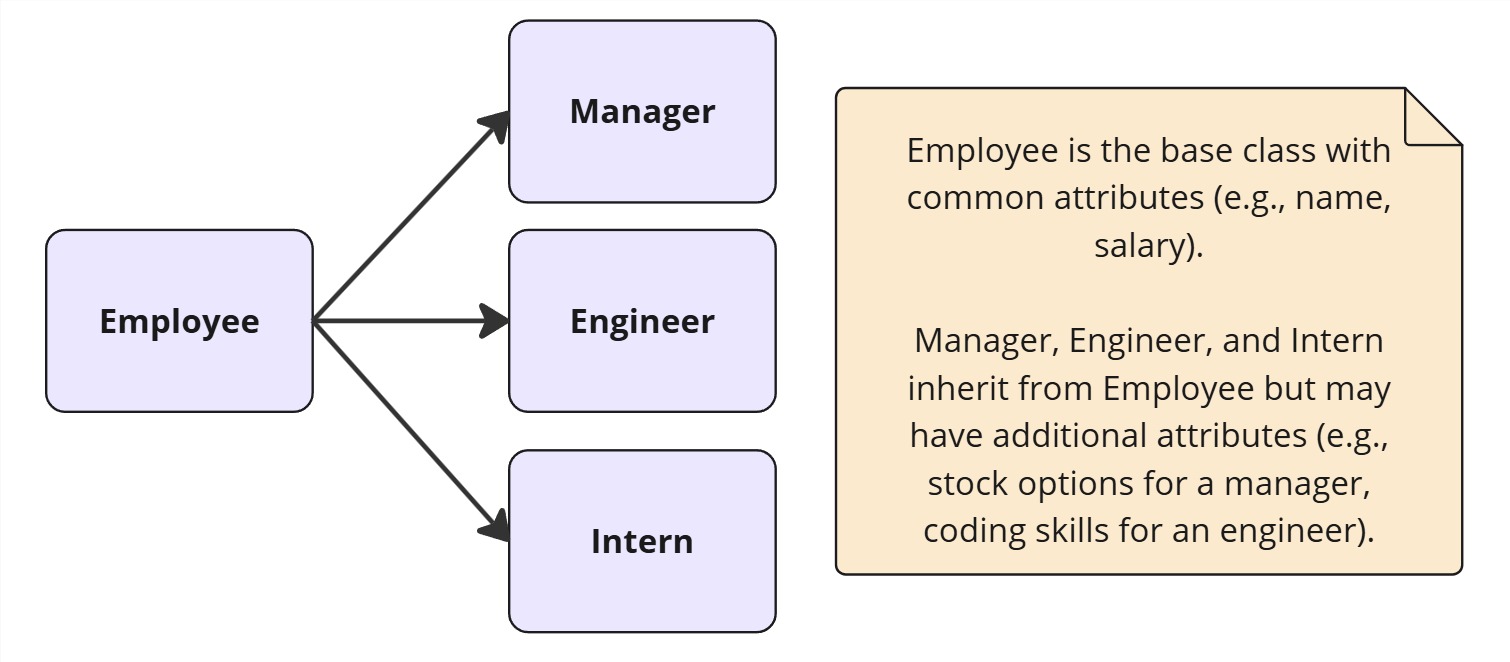
Design Patterns Using Inheritance
- Template Method Pattern: Defines a skeleton of an algorithm in a base class and lets subclasses override specific steps. Template Method pattern relies on inheritance, where a base class defines a framework for an operation and derived classes provide specific implementations for certain steps.
- Factory Method Pattern: Uses inheritance to delegate object creation to subclasses.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Association | Aggregation | Composition | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relationship between two independent classes | “Has-a” relationship | “Part-of” relationship | “Is-a” relationship between parent and child classes |
| Dependency | No dependency | Weak dependency | Strong dependency | Strong dependency |
| Lifecycle | Objects can exist independently | Objects can exist independently | Objects cannot exist independently | Subclass depends on superclass |
| Ownership | No ownership | No strict ownership | Strong ownership | Hierarchical ownership |
| Strength | Weak | Medium | Strong | Strong |
| Cardinality | One-to-one, One-to-many, Many-to-many, Many-to-one | One-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many | One-to-one, One-to-many | One-to-one |
| Representation | Uses a direct reference | Uses a reference to the contained object(s) | Contains instances of the contained object(s) | Derived class extends base class |
Conclusion
Understanding how classes relate to each other is fundamental in object-oriented design. The choice between association, aggregation, composition, and inheritance impacts modularity, reusability, and maintainability.
- Use association when objects interact but don’t depend on each other.
- Use aggregation when one object contains another, but they can exist separately.
- Use composition when objects have a strict lifecycle dependency.
- Use inheritance to model an “is-a” relationship between classes.
Many design patterns leverage these relationships to create reusable and flexible software architectures. By choosing the right relationship model, you can design scalable and maintainable systems.
