Apache Kafka Essential Commands and Concepts
- 7 minsKafka Topics and Essential Commands
Apache Kafka is a powerful distributed event streaming platform designed for high-throughput and fault-tolerant data processing. Whether setting up a single-node instance for development or configuring a multi-node cluster for production, understanding Kafka’s core commands is crucial.
This post breaks down the following topics:
-
Zookeeper
-
Start and configure Kafka brokers
-
Create and manage topics
-
Produce and consume messages
-
Set up consumer groups for efficient data processing
Zookeeper
Apache Zookeeper is a distributed coordination service that helps manage and synchronize distributed applications like Kafka. It provides features like:
- Leader Election – Helps distributed systems choose a leader.
- Configuration Management – Stores and updates configurations across nodes.
- Service Discovery – Tracks available services in a cluster.
- Distributed Locks – Prevents multiple processes from modifying the same resource.
- Metadata Storage – Stores Kafka topic details, brokers, and partitions.
So zookeeper is a kind of database where Kafka brokers store a bunch of shared information. It is used as a shared system among multiple Kafka brokers to coordinate among themselves for various things. Kafka needs zookeeper for coordinating things among the brokers, and you must have it running even if you have got a single broker.
⚠️ Note: Kafka no longer requires Zookeeper in newer versions (Kafka KRaft mode replaces it). 🔹 If using Kafka < 3.0, you must use Zookeeper. 🔹 If using Kafka 3.0+, you can use Kafka KRaft mode (Zookeeper-free mode).
Kafka Startup
The Command:
bin\windows\kafka-server-start.bat config\server.properties
This command launches a Kafka server (broker) with the settings specified in server.properties. Let’s analyze each part of it.
1. bin\windows\
This is the directory where Kafka’s Windows scripts are stored. On Linux/macOS, you would typically use the bin/ directory instead.
2. kafka-server-start.bat
This is the batch script that starts the Kafka broker. Internally, it:
- Calls Java to run Kafka’s main server process.
- Uses the provided configuration file to determine how Kafka should operate.
3. config\server.properties
This is the configuration file that defines important settings for the Kafka broker, including:
- Broker ID (
broker.id=0) – A unique identifier for this Kafka instance. - Listeners (
listeners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9092) – Specifies how clients connect to Kafka. - Log Directory (
log.dirs=C:/kafka-logs) – Defines where Kafka stores its data. - Zookeeper Connection (
zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181) – Specifies how Kafka connects to Zookeeper (for older versions of Kafka).
What Happens When You Run the Command?
- Kafka starts using the settings in
server.properties. - If using Zookeeper mode, the broker registers itself with Zookeeper.
- Kafka opens its listener port (default:
9092) for clients to connect. - It creates or recovers partitions and topics from its logs.
- The Kafka server is now ready to handle producer and consumer requests.
Configuring Multiple Brokers
When starting a Kafka broker, we supply the server.properties file as an argument. The kafka-server-start command reads configurations from this file. If we plan to run multiple brokers, we need to:
- Make copies of
server.properties– Each broker requires a separate configuration file with a unique name. - Modify essential configurations – Each broker must have unique settings.
Key Configuration Changes
1. Unique Broker ID
broker.id=0 # Must be unique for each broker
Each broker needs a distinct broker.id, which uniquely identifies it within the cluster.
2. Listener Port
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
- If commented out, Kafka defaults to port
9092. - This is the port that producers use to send data and consumers use to retrieve data.
- For multiple brokers on the same machine, assign different ports:
- Broker 0: Port
9092 - Broker 1: Port
9093 - Broker 2: Port
9094
- Broker 0: Port
3. Log Directory
log.dirs=/path/to/kafka-logs-0
Each broker needs a separate log directory to prevent conflicts. Example:
- Broker 0:
/var/log/kafka-logs-0 - Broker 1:
/var/log/kafka-logs-1 - Broker 2:
/var/log/kafka-logs-2
Running Kafka on Multiple Machines
When running multiple brokers on different machines, the only required change is assigning a unique broker.id. Kafka can also be configured to auto-assign IDs, eliminating the need for manual changes.
By correctly configuring multiple brokers, you can create a robust, scalable Kafka cluster ready to handle high-throughput data streams.
Managing Kafka Topics
Once Kafka is running, you need to create topics for storing and processing messages. The following command creates a new topic:
bin\windows\kafka-topics.bat --create --topic my-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1
Command Breakdown
1. bin\windows\kafka-topics.bat
This script is used to manage Kafka topics on Windows. It’s located in the Kafka installation directory under bin\windows.
2. --create
This flag tells Kafka to create a new topic.
3. --topic my-topic
Specifies the name of the topic to be created (my-topic in this case).
4. --partitions 1
Defines the number of partitions for the topic.
5. --replication-factor 1
Defines the number of copies (replicas) of the topic’s data across different brokers.
6. --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Specifies the Kafka broker(s) to connect to for topic creation.
Other Useful Commands
List all topics
bin\windows\kafka-topics.bat --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
This command lists all available topics in the Kafka cluster.
Describe a topic (Check details)
bin\windows\kafka-topics.bat --describe --topic my-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
This command provides detailed information about a topic, such as its partitions, leader, replicas, and in-sync replicas (ISR).
Produce Events (Write to a Topic)
bin\windows\kafka-console-producer.bat --topic my-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 <..\data\file.csv>
Command Breakdown
bin\windows\kafka-console-producer.bat: This script creates a Kafka producer on Windows.--topic my-topic: Specifies the topic name to send data to.--bootstrap-server localhost:9092: Defines the Kafka broker coordinates.<..\data\file.csv>: Redirects file content as input to the producer.
Consume Events (Read from a Topic)
bin\windows\kafka-console-consumer.bat --topic my-topic --from-beginning --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Command Breakdown
bin\windows\kafka-console-consumer.bat: This script creates a Kafka consumer on Windows.--topic my-topic: Specifies the topic to read from.--from-beginning: Reads messages from the beginning.--bootstrap-server localhost:9092: Defines the Kafka broker coordinates.
These commands help manage data flow within Kafka by producing and consuming messages efficiently.
Consumer Groups
Consumers reading from the same topic can share the load.
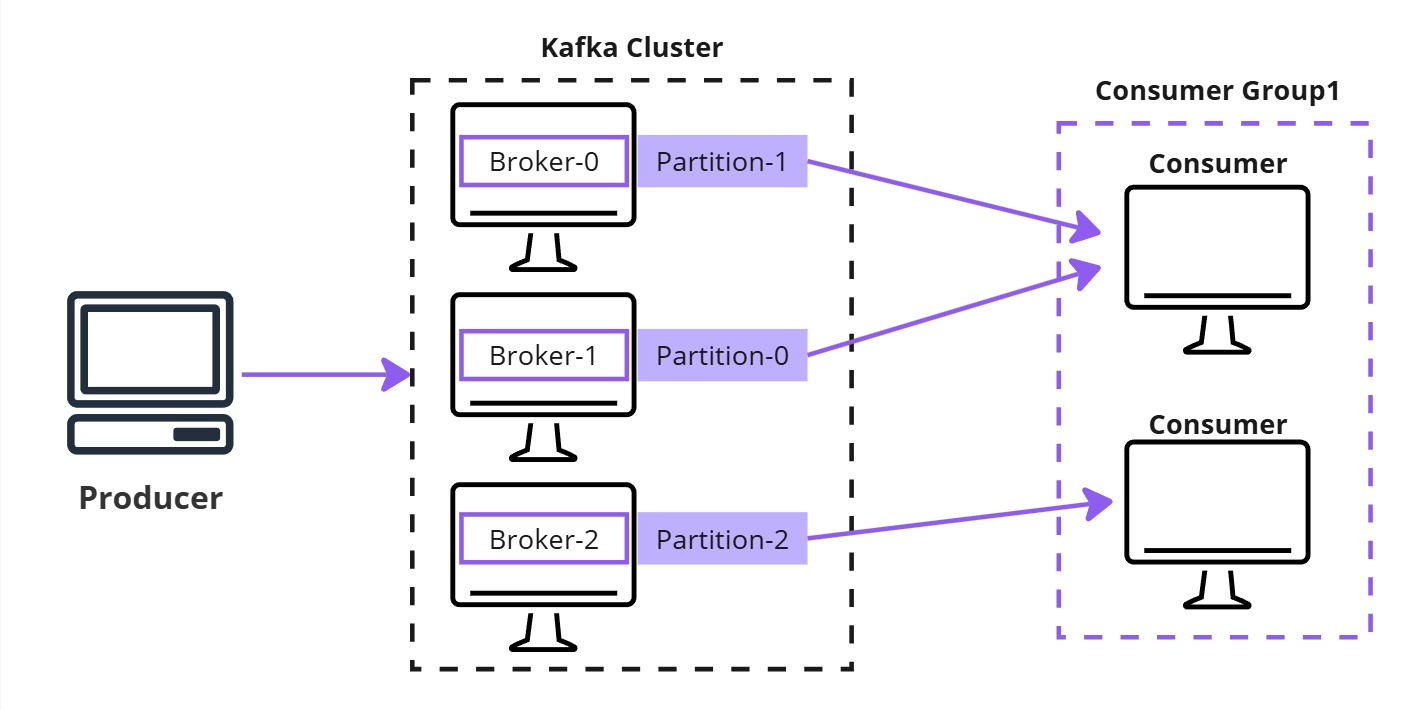
Example:
- 1 console producer
- 3-node Kafka cluster
- 1 topic with 3 partitions
- 2 consumers running in a group and waiting to read data from these partitions
The data goes to the Kafka topic. Since the topic is partitioned, all the data will be distributed among the three partitions. Some records will go to the first broker in the first partition, while others will be distributed across the other two brokers and partitions.
However, since we have 2 consumers in the group and 3 partitions, one consumer will read from 2 partitions, while the other will read from the remaining partition. This ensures all data is processed efficiently.
